🎯 Mục tiêu bài học
Sau bài học này, học viên sẽ:
✅ Hiểu tại sao Ensemble methods hiệu quả
✅ Nắm vững Bagging và Random Forest
✅ Hiểu các thuật toán Boosting: AdaBoost, Gradient Boosting, XGBoost
✅ Biết cách sử dụng Stacking
Thời gian: 5-6 giờ | Độ khó: Theory
� Bảng Thuật Ngữ Quan Trọng
| Thuật ngữ | Tiếng Việt | Giải thích đơn giản |
|---|---|---|
| Ensemble | Kết hợp | Gom nhiều model để dự đoán tốt hơn |
| Bagging | Bootstrap Aggregating | Train song song trên bootstrap samples |
| Boosting | Tăng cường | Train tuần tự, mỗi model sửa lỗi trước |
| Random Forest | Rừng ngẫu nhiên | Bagging + random feature subset |
| Gradient Boosting | GB | Boosting dựa trên gradient của loss |
| XGBoost | eXtreme GB | GB tối ưu hóa với regularization |
| LightGBM | Light GB | GB nhanh dùng leaf-wise growth |
| Stacking | Xếp chồng | Dùng meta-model kết hợp outputs |
| Feature Importance | Độ quan trọng feature | Đo mức đóng góp của từng feature |
Checkpoint
Bạn đã đọc qua bảng thuật ngữ? Hãy ghi nhớ chúng!
�📊 Tổng quan Ensemble Methods
1. Tổng quan Ensemble Methods
1.1 Ý tưởng chính
"Wisdom of the Crowd" - Kết hợp nhiều model yếu thành model mạnh.
| Bước | Mô tả |
|---|---|
| 1 | Dữ liệu đầu vào |
| 2 | Train nhiều models (parallel hoặc sequential) |
| 3 | Kết hợp predictions |
| 4 | Final prediction |
1.2 Tại sao Ensemble hiệu quả?
| Lợi ích | Giải thích |
|---|---|
| Giảm Variance | Bagging |
| Giảm Bias | Boosting |
| Kết hợp đa dạng | Stacking |
1.3 Các loại Ensemble
| Method | Cách hoạt động | Ví dụ |
|---|---|---|
| Bagging | Train parallel, vote | Random Forest |
| Boosting | Train sequential, fix errors | XGBoost, LightGBM |
| Stacking | Train meta-model | Custom |
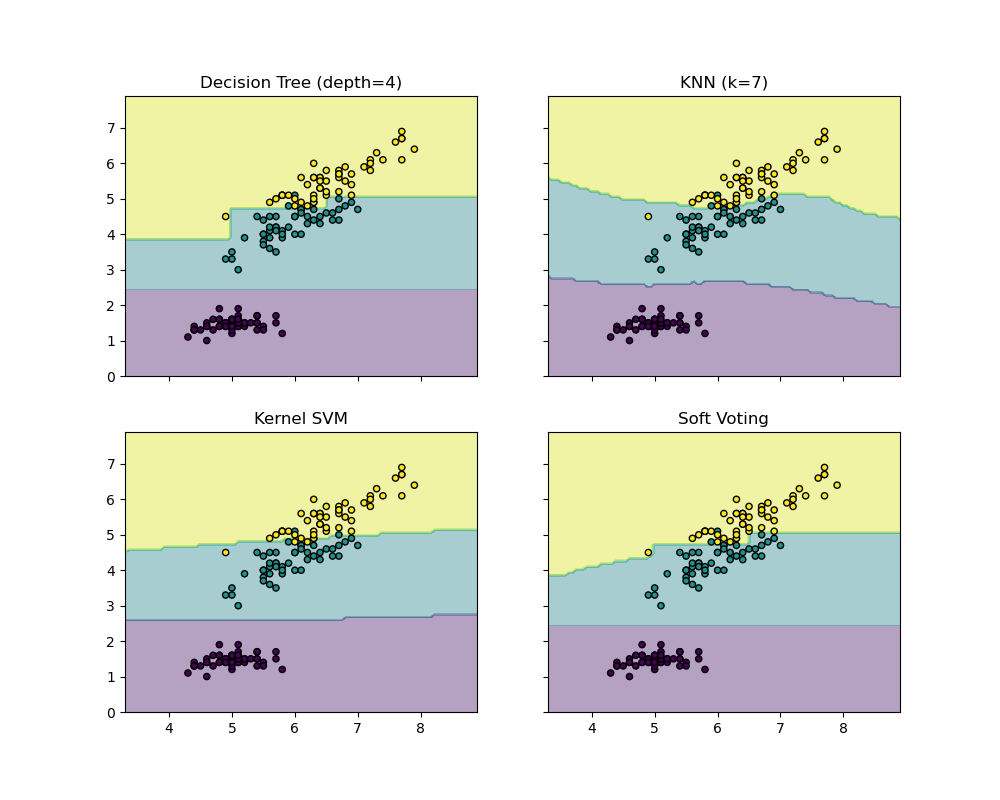
Hinh: Voting Classifier - kết hợp predictions từ nhiều models
📦 Bagging (Bootstrap Aggregating)
2. Bagging (Bootstrap Aggregating)
2.1 Thuật toán
| Bước | Mô tả |
|---|---|
| 1 | Original Dataset |
| 2 | Tạo nhiều Bootstrap Samples (lấy mẫu có hoàn lại) |
| 3 | Train model riêng biệt trên mỗi sample |
| 4 | Voting (classification) hoac Averaging (regression) |
| 5 | Final Prediction |
Bootstrap Sampling: Lấy mẫu có hoàn lại từ training data.
2.2 Công thức Voting
Classification (Hard Voting):
Regression (Averaging):
🌲 Random Forest
3. Random Forest
3.1 Cải tiến từ Bagging
Random Forest = Bagging + Feature Randomness
Mỗi tree:
- Train trên bootstrap sample
- Chọn random subset features tại mỗi split
3.2 Hyperparameters quan trọng
| Parameter | Ý nghĩa | Typical |
|---|---|---|
| n_estìmators | Số trees | 100-500 |
| max_depth | Độ sâu tree | 10-30 |
| max_features | Số features mỗi split | sqrt(n) |
| min_samples_split | Min samples để split | 2-10 |
3.3 Vi du tinh toan
Giả sử có 3 trees vote:
| Sample | Tree 1 | Tree 2 | Tree 3 | Final |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| x1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| x2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| x3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
Soft Voting với probabilities:
| Sample | Tree 1 P(1) | Tree 2 P(1) | Tree 3 P(1) | Avg | Final |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x1 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.4 | 0.63 | 1 |
| x2 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 0.37 | 0 |
Checkpoint
Bạn có thể giải thích Random Forest khác Bagging thông thường ở điểm nào không?
💻 Thực hành Random Forest
4. Thuc hanh Random Forest
4.1 Classification
1from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier2from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, GridSearchCV3from sklearn.metrics import classification_report, confusion_matrix4import numpy as np56# Load data7from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer8data = load_breast_cancer()9X, y = data.data, data.target1011X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(12 X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=4213)1415# Basic Random Forest16rf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estìmators=100, random_state=42)17rf.fit(X_train, y_train)1819# Evaluate20y_pred = rf.predict(X_test)21print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred))2223# Feature Importance24importance = rf.feature_importances_25indices = np.argsort(importance)[::-1][:10]2627print("\nTop 10 Features:")28for i, idx in enumerate(indices):29 print(f"{i+1}. {data.feature_names[idx]}: {importance[idx]:.4f}")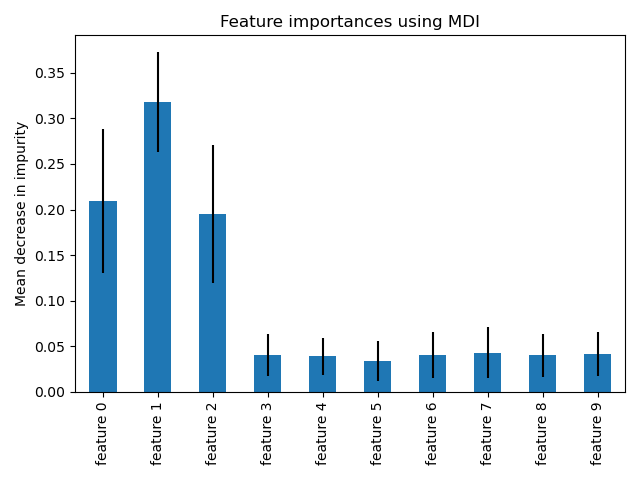
Hinh: Feature Importance từ Random Forest
4.2 Hyperparameter Tuning
1param_grid = {2 'n_estìmators': [100, 200, 300],3 'max_depth': [10, 20, None],4 'min_samples_split': [2, 5, 10],5 'max_features': ['sqrt', 'log2']6}78grid_search = GridSearchCV(9 RandomForestClassifier(random_state=42),10 param_grid, cv=5, scoring='f1', n_jobs=-111)12grid_search.fit(X_train, y_train)1314print(f"Best params: {grid_search.best_params_}")15print(f"Best CV F1: {grid_search.best_score_:.4f}")🚀 Boosting
5. Boosting
5.1 Ý tưởng chinh
Train models tuần tự, mỗi model sửa lỗi của model trước.
| Bước | Mô tả |
|---|---|
| 1 | Train Model 1 |
| 2 | Xác định Errors từ Model 1 |
| 3 | Model 2 tập trung vào Errors 1 |
| 4 | Xác định Errors từ Model 2 |
| 5 | Model 3 tập trung vào Errors 2 |
| ... | Tiếp tục |
5.2 AdaBoost
Adaptive Boosting:
- Tăng weight cho samples bi classify sai
- Model sau focus vào samples khó
Công thức weight update:
Final prediction:
5.3 Gradient Boosting
Thay vi adjust weights, train model moi tren residuals (sai số).
Thuật toán:
| Bước | Mô tả |
|---|---|
| 0 | Khoi tao: |
| 1 | Tính residuals: |
| 2 | Train tree tren residuals |
| 3 | Update: |
| 4 | Lap lai |
📝 Ví dụ Gradient Boosting thủ công
6. Vi du Gradient Boosting thu cong
6.1 Data
| 1 | 2.5 |
| 2 | 3.5 |
| 3 | 3.0 |
| 4 | 5.5 |
6.2 Iteration 0
Residuals:
| 1 | 2.5 | 3.625 | -1.125 |
| 2 | 3.5 | 3.625 | -0.125 |
| 3 | 3.0 | 3.625 | -0.625 |
| 4 | 5.5 | 3.625 | 1.875 |
6.3 Iteration 1
Train simple tree tren residuals:
- Gia su: ,
Update voi learning rate :
| 1 | 3.625 | -0.625 | 3.562 |
| 2 | 3.625 | -0.625 | 3.562 |
| 3 | 3.625 | 0.625 | 3.687 |
| 4 | 3.625 | 0.625 | 3.687 |
Residuals moi giam! Tiếp tục them nhieu iterations...
⚡ XGBoost
7. XGBoost
7.1 Cai tien
| Cai tien | Mô tả |
|---|---|
| Regularization | L1, L2 de tranh overfitting |
| Parallel processing | Nhanh hon |
| Handling missing values | Tu dong |
Objective:
7.2 Hyperparameters quan trọng
| Parameter | Ý nghĩa | Typical |
|---|---|---|
| n_estìmators | Số trees | 100-1000 |
| learning_rate (eta) | Learning rate | 0.01-0.3 |
| max_depth | Độ sâu tree | 3-10 |
| subsample | Row sampling | 0.6-1.0 |
| colsample_bytree | Feature sampling | 0.6-1.0 |
| reg_lambda (L2) | L2 regularization | 1-10 |
7.3 Thuc hanh XGBoost
1import xgboost as xgb2from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split3from sklearn.metrics import classification_report45# Prepare data6X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2)78# XGBoost Classifier9xgb_clf = xgb.XGBClassifier(10 n_estìmators=200,11 learning_rate=0.1,12 max_depth=5,13 subsample=0.8,14 colsample_bytree=0.8,15 reg_lambda=1,16 random_state=42,17 eval_metric='logloss'18)1920# Early Stopping21xgb_clf.fit(22 X_train, y_train,23 eval_set=[(X_test, y_test)],24 verbose=False25)2627# Evaluate28y_pred = xgb_clf.predict(X_test)29print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred))3031# Feature Importance32xgb.plot_importance(xgb_clf, max_num_features=10)Checkpoint
Bạn có thể giải thích XGBoost cải tiến gì so với Gradient Boosting không?
🔄 So sánh Ensemble Methods
8. So sanh Ensemble Methods
| Method | Bias | Variance | Toc do | Overfitting |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Random Forest | Medium | Low | Fast | It |
| AdaBoost | Low | Medium | Medium | Co the |
| Gradient Boosting | Low | Medium | Slow | Co the |
| XGBoost | Low | Low | Fast | It (regularized) |
8.1 Khi nào dùng gi?
| Tính huong | Chọn |
|---|---|
| Data lon | XGBoost/LightGBM |
| Data nho | Random Forest |
| Can interpretability | Random Forest |
| Toc do quan trong | XGBoost/LightGBM |
| Don gian, stable | Random Forest |
📚 Model Stacking
9. Model Stacking
9.1 Ý tưởng
Su dung meta-model de combine predictions tu base models.
| Layer | Mô tả |
|---|---|
| Layer 1 | Base Models (RF, XGBoost, LR...) |
| Layer 2 | Meta Features (predictions tu Layer 1) |
| Layer 3 | Meta Model |
| Output | Final Prediction |
9.2 Thuc hanh Stacking
1from sklearn.ensemble import StackingClassifier, RandomForestClassifier2from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression3from sklearn.svm import SVC4import xgboost as xgb56# Define base models7base_models = [8 ('rf', RandomForestClassifier(n_estìmators=100, random_state=42)),9 ('xgb', xgb.XGBClassifier(n_estìmators=100, random_state=42)),10 ('svc', SVC(probability=True, random_state=42))11]1213# Stacking with Logistic Regression as meta model14stacking_clf = StackingClassifier(15 estìmators=base_models,16 final_estìmator=LogisticRegression(),17 cv=518)1920stacking_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)21y_pred = stacking_clf.predict(X_test)2223print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred))⚡ LightGBM (Bonus)
10. LightGBM (Bonus)
10.1 Cai tien so voi XGBoost
| Cai tien | Mô tả |
|---|---|
| Histogram-based | Nhanh hon |
| Leaf-wise growth | Hieu qua hon |
| Categorical features | Native support |
1import lightgbm as lgb23lgb_clf = lgb.LGBMClassifier(4 n_estìmators=200,5 learning_rate=0.1,6 max_depth=5,7 num_leaves=31,8 random_state=429)1011lgb_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)12y_pred = lgb_clf.predict(X_test)13print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred))📝 Bài tập tự luyện (Phần 1)
Bài tập tự luyện
- Bài tập 1: So sánh Random Forest, XGBoost, LightGBM trên cùng dataset
- Bài tập 2: Implement simple Bagging từ đầu
- Bài tập 3: Tạo Stacking model với 4 base models khác nhau
- Bài tập 4: Tune hyperparameters của Random Forest với GridSearchCV
- Bài tập 5: Implement Gradient Boosting thủ công (3 iterations)
📊 Metrics cho Regression với Ensemble
11. Metrics cho Regression với Ensemble
11.1 Regression Metrics quan trọng
| Metric | Công thức | Ý nghĩa | Khi nào dùng |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | Trung bình sai số tuyệt đối | Muốn hiểu error magnitude, không punish outliers | |
| MSE | Trung bình sai số bình phương | Outliers quan trọng, cần punish | |
| RMSE | Root MSE (cùng đơn vị với y) | Dễ interpret, cùng scale với target | |
| R² | % variance explained | Đánh giá overall fit (1.0 = perfect) |
11.2 Ví dụ Regression với Random Forest
1from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor2from sklearn.datasets import fetch_california_housing3from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split4from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, mean_absolute_error, r2_score5import numpy as np67# 1. Load Data8housing = fetch_california_housing()9X, y = housing.data, housing.target1011# 2. Split12X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(13 X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=4214)1516# 3. Train Random Forest Regressor17rf_reg = RandomForestRegressor(18 n_estimators=200,19 max_depth=15,20 min_samples_split=5,21 max_features='sqrt',22 random_state=42,23 n_jobs=-124)25rf_reg.fit(X_train, y_train)2627# 4. Predict28y_pred = rf_reg.predict(X_test)2930# 5. Evaluation31mae = mean_absolute_error(y_test, y_pred)32mse = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred)33rmse = np.sqrt(mse)34r2 = r2_score(y_test, y_pred)3536print("=== Regression Metrics ===")37print(f"MAE: {mae:.4f}")38print(f"MSE: {mse:.4f}")39print(f"RMSE: {rmse:.4f}")40print(f"R²: {r2:.4f}")4142# 6. Feature Importance43importances = pd.DataFrame({44 'feature': housing.feature_names,45 'importance': rf_reg.feature_importances_46}).sort_values('importance', ascending=False)4748print("\n=== Feature Importances ===")49print(importances)Output mẫu:
1=== Regression Metrics ===2MAE: 0.32453MSE: 0.25364RMSE: 0.50365R²: 0.81566 7Feature Importances:8 feature importance90 MedInc 0.5234101 Longitude 0.1456112 Latitude 0.112312...🔄 So sánh chi tiết GB vs RF
12. So sánh chi tiết GB vs RF
12.1 Bảng so sánh toàn diện
| Tiêu chí | Random Forest (Bagging) | Gradient Boosting |
|---|---|---|
| Cơ chế | Parallel trees, averaging | Sequential trees, error correction |
| Bias | Medium | Low |
| Variance | Low (averaging giảm variance) | Medium (có thể overfit) |
| Tốc độ train | Nhanh (parallel) | Chậm (sequential) |
| Overfitting | Ít (robust) | Dễ (nếu không tune) |
| Hyperparameter | Ít nhạy cảm | Rất nhạy cảm |
| Interpretability | Feature importance rõ | Khó visualize |
| Noisy data | Robust | Nhạy cảm (fit noise) |
| Khi nào dùng | Quick baseline, stable | Maximize accuracy, có thời gian tune |
12.2 Bias-Variance Trade-off
Mối quan hệ Bias-Variance:
-
Random Forest (Bagging): Low Bias + Low Variance
- Averaging nhiều trees giảm variance
- Mỗi tree có full depth nên low bias
-
Gradient Boosting: Very Low Bias + Medium Variance
- Sequential learning giảm bias hiệu quả
- Có thể overfit nếu không regularize
Trade-off:
- Bagging tập trung giảm Variance → Tránh overfitting
- Boosting tập trung giảm Bias → Tăng accuracy nhưng risk overfit
⚠️ Common Mistakes & Best Practices
13. Common Mistakes & Best Practices
13.1 Sai lầm thường gặp
| Lỗi | Mô tả | Hậu quả | Giải pháp |
|---|---|---|---|
| High LR + High Estimators | Learning rate cao + nhiều trees | Overfitting nhanh | Giảm LR khi tăng n_estimators |
| Deep Trees trong GB | max_depth quá lớn trong Gradient Boosting | Overfit từng iteration | Giữ max_depth = 3-8 cho GB |
| Không tune | Dùng default parameters | Performance kém | Luôn GridSearch/RandomSearch |
| Không cross-validate | Chỉ train/test split | Không stable | Dùng 5-fold CV |
| Fit noisy data | GB cố fit cả outliers | Model học noise | Clean data trước, dùng robust loss |
| Không scale trong RF | Nghĩ RF không cần scaling | Không ảnh hưởng lắm | OK cho RF, nhưng nên scale cho consistency |
13.2 Best Practices
Random Forest:
1# ✅ Good Practice2rf = RandomForestClassifier(3 n_estimators=200, # Nhiều trees = stable4 max_depth=15, # Limit depth tránh overfit5 min_samples_split=10, # Regularization6 max_features='sqrt', # Feature randomness7 n_jobs=-1, # Parallel processing8 random_state=42, # Reproducibility9 oob_score=True # Out-of-bag validation10)Gradient Boosting:
1# ✅ Good Practice2gb = GradientBoostingClassifier(3 n_estimators=100, # Moderate số trees4 learning_rate=0.1, # Vừa phải5 max_depth=5, # Shallow trees6 subsample=0.8, # Stochastic GB7 min_samples_split=10, # Regularization8 validation_fraction=0.2, # Early stopping9 n_iter_no_change=10, # Stop if no improve10 random_state=4211)🎯 When to Use What?
14. When to Use What?
14.1 Decision Tree cho từng scenario
| Scenario | Recommendation | Lý do |
|---|---|---|
| Quick baseline | Random Forest | Nhanh, robust, ít tune |
| Maximum accuracy | XGBoost/LightGBM | SOTA cho tabular data |
| Large dataset (>1M) | LightGBM | Fastest, memory efficient |
| Small dataset (<10k) | Random Forest | Ít overfit hơn |
| Interpretability needed | Random Forest | Feature importance rõ |
| Kaggle competition | XGBoost + Stacking | Proven winner |
| Production speed | LightGBM | Fast inference |
| Imbalanced data | XGBoost (scale_pos_weight) | Built-in handling |
| Noisy data | Random Forest | Robust to outliers |
| Time series | Gradient Boosting | Sequential nature fits |
14.2 Workflow Decision Tree
Quy trình lựa chọn thuật toán:
- Need quick baseline? → YES → Random Forest
- Have time to tune? → NO → Random Forest
- Data > 1M rows? → YES → LightGBM
- Need max accuracy? → YES → XGBoost + GridSearch
- Default choice → Random Forest
📉 Gradient Boosting Chi tiết từ PDF
15. Gradient Boosting - Chi tiết từ PDF
15.1 Loss Functions cho Regression
| Loss | Công thức | Khi nào dùng | Residuals |
|---|---|---|---|
| MSE (L2) | Standard regression | ||
| MAE (L1) | Robust to outliers | ||
| Huber | Hybrid L1/L2 | Robust & differentiable | Conditional |
15.2 Loss Function cho Classification
Log Loss (Cross Entropy):
Probability từ Log Odds:
Residuals:
15.3 Regularization trong Gradient Boosting
Learning Rate (Shrinkage):
- High LR (0.3-1.0): Fast convergence, risk overshoot
- Low LR (0.01-0.1): Steady, needs more trees
- Rule: Lower LR → More n_estimators
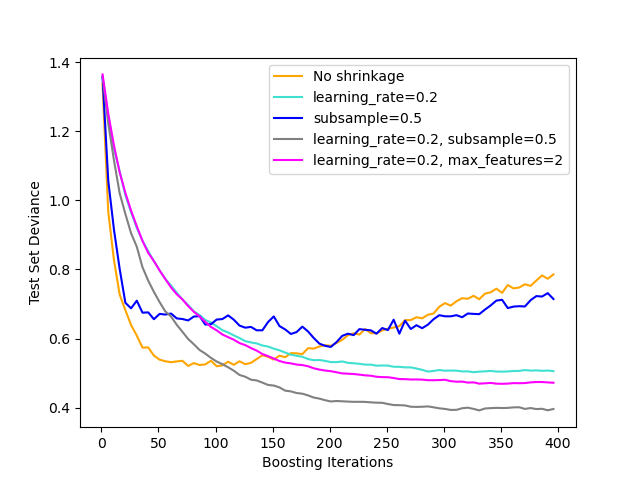
Subsample (Stochastic GB):
- Train each tree on random subset
- Typical: 0.5-0.8
- Giảm overfitting, tăng robustness
⏰ Advanced: Early Stopping
16. Advanced: Early Stopping
16.1 Gradient Boosting với Early Stopping
1from sklearn.ensemble import GradientBoostingClassifier2from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split34# Split thêm validation set5X_train, X_temp, y_train, y_temp = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3)6X_val, X_test, y_val, y_test = train_test_split(X_temp, y_temp, test_size=0.5)78# Gradient Boosting với early stopping9gb = GradientBoostingClassifier(10 n_estimators=1000, # Nhiều trees11 learning_rate=0.05, # Low LR12 max_depth=5,13 validation_fraction=0.2, # 20% for early stopping14 n_iter_no_change=20, # Stop if no improve in 20 iterations15 tol=0.0001, # Tolerance16 verbose=1,17 random_state=4218)1920gb.fit(X_train, y_train)2122print(f"Best iteration: {gb.n_estimators_}")23print(f"Training stopped at: {gb.n_estimators_}")📝 Tổng Kết
Key Takeaways:
- 🌲 Random Forest = Bagging + random features, chống overfitting tốt
- 🚀 Gradient Boosting = train tuần tự, hiệu năng cao nhưng cần tune
- ⚡ XGBoost / LightGBM là top choice cho tabular data
- 📚 Stacking kết hợp đa dạng models với meta-learner
- 💻 Scikit-learn:
RandomForestClassifier(),GradientBoostingClassifier(),StackingClassifier()
Bài tập tự luyện
- Bài tập 1: So sánh Random Forest, XGBoost, LightGBM trên cùng dataset
- Bài tập 2: Implement simple Bagging từ đầu (10 bootstrap samples)
- Bài tập 3: Tạo Stacking model với 4 base models khác nhau
- Bài tập 4: Regression với California Housing (RF Regressor)
- Bài tập 5: Gradient Boosting thủ công (3 iterations)
Tài liệu tham khảo
| Nguồn | Link |
|---|---|
| Scikit-learn Ensemble | scikit-learn.org |
| XGBoost Docs | xgboost.readthedocs.io |
| LightGBM Docs | lightgbm.readthedocs.io |
| StatQuest - Random Forest | youtube.com |
| StatQuest - Gradient Boost | youtube.com |
| Gradient Boosting Explained | explained.ai |
Câu hỏi tự kiểm tra
- Bagging và Boosting khác nhau như thế nào về cách kết hợp các base models?
- Random Forest cải tiến gì so với Bagging thông thường? Tại sao random feature subset giúp giảm overfitting?
- XGBoost và LightGBM khác nhau như thế nào? Khi nào nên dùng mỗi loại?
- Stacking hoạt động như thế nào? Meta-learner đóng vai trò gì trong Stacking?
🎉 Tuyệt vời! Bạn đã hoàn thành bài học Ensemble Methods!
Tiếp theo: Cùng làm Quiz tổng hợp — ôn tập và kiểm tra toàn bộ kiến thức khóa học!
Checkpoint
Bạn đã nắm vững Ensemble Methods chưa? Sẵn sàng cho Quiz tổng hợp!
